Have you ever looked at Cortex M4 instruction set ? There is a particular one that does not seem like much but can do some magic !
I’m talking about SEL intrinsic and this article will show one of its possible usage in a Min/Max detection algorithm.
Basic C Min/Max detection
Let’s start with a C implementation. Same logic can be applied on both 8- and 16-bits buffers.
C generic implementation
#ifdef DATA_8 typedef int8_t s_data_t; typedef uint16_t u_pair_t; #else //DATA_16 typedef int16_t s_data_t; typedef uint32_t u_pair_t; #endif typedef union { struct { s_data_t min; s_data_t max; }fields; u_pair_t pair; } MinMax_t; MinMax_t SearchMinMax_C(s_data_t* pSrc, int32_t pSize) { s_data_t data, min, max; MinMax_t out; data = *pSrc++; min = data; max = data; while (--pSize > 0) { data = *pSrc++; if (data < min) { min = data; } if (data > max) { max = data; } } out.fields.min = min; out.fields.max = max; return out; }
This very straight-forward implementation is already pretty efficient thanks to Thumb-2 instruction IT (If-Then) that allows conditional execution and removes branches. Here si the detail of Keil compiler output (ARM Compiler V5.04.0.49 Evaluation).
8-bits Optimized compiler output (-O3 -Otime)
; Bytes Cycles Comment SearchMinMaxC: ; - 3 Function call LDRSB r2,[r0],#0x01 ; 4 2 Load from post-incremented sample pointer and update it SUBS r1,r1,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter MOV r3,r2 ; 2 1 Copy loaded data to Max register CMP r1,#0x00 ; 2 1 Test if we need to loop BLE final ; 2 1,3 Go through (1 cycle) or loop (3 cycles) loop: LDRSB r12,[r0],#0x01 ; 4 2 Load from post-incremented sample pointer and update it CMP r3,r12 ; 2 1 Compare new sample to max IT GT ; 2 1 Execute following Move if new sample is bigger MOVGT r3,r12 ; 2 1 Conditionally Store new sample in Max register CMP r2,r12 ; 2 1 Compare new sample to min IT LT ; 2 1 Execute following Move if new sample is smaller MOVLT r2,r12 ; 2 1 Conditionally Store new sample in Min register SUBS r1,r1,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter BNE loop ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) final: UXTB r0,r3 ; 2 1 Keep only 8 lower bits of Max value and put them in return register BFI r0,r2,#8,#8 ; 4 1 Put 8 lower bits of Min value in byte 1 of return register BX lr ; 2 3 Return ROM : 40 bytes Stack : 0 bytes Cycles : 9 + 12 * (N - 2) + 10 + 5
16-bits Optimized compiler output (-O3 -Otime)
; Bytes Cycles Comment SearchMinMaxC: ; - 3 Function call LDRSH r2,[r0],#0x02 ; 4 2 Load from post-incremented sample pointer and update it SUBS r1,r1,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter MOV r3,r2 ; 2 1 Copy loaded data to Max register CMP r1,#0x00 ; 2 1 Test if we need to loop BLE final ; 2 1,3 Go through (1 cycle) or loop (3 cycles) loop: LDRSH r12,[r0],#0x02 ; 4 2 Load from post-incremented sample pointer and update it CMP r3,r12 ; 2 1 Compare new sample to max IT GT ; 2 1 Execute following Move if new sample is bigger MOVGT r3,r12 ; 2 1 Conditionally Store new sample in Max register CMP r2,r12 ; 2 1 Compare new sample to min IT LT ; 2 1 Execute following Move if new sample is smaller MOVLT r2,r12 ; 2 1 Conditionally Store new sample in Min register SUBS r1,r1,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter BNE loop ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) final: BFI r0,r3,#0,#16 ; 4 1 Put 16 lower bits of Max value in return register low halfword BFI r0,r2,#16,#16 ; 4 1 Put 16 lower bits of Min value in return register high halfword BX lr ; 2 3 Return ROM : 42 bytes Stack : 0 bytes Cycles : 9 + 12 * (N - 2) + 10 + 5
Parallel instructions study
Now, let’s add some DSP magic in there !
SEL instruction independently selects bytes from one of two registers based on corresponding APSR GE bit:
/* Usage :*/ /* Asm */ SEL Rd, Rn, Rm /* C */ Rd = __SEL(Rn, Rm); /* Let's write a 32 bit register the following : Rx = B3 | B2 | B1 | B0 where B3 is the MSByte and B0 the LSByte */ Rd.B3 = (GE[3] == 1) ? Rn.B3 : Rm.B3; Rd.B2 = (GE[2] == 1) ? Rn.B2 : Rm.B2; Rd.B1 = (GE[1] == 1) ? Rn.B1 : Rm.B1; Rd.B0 = (GE[0] == 1) ? Rn.B0 : Rm.B0;
Both Signed parallel byte-wise subtraction (SSUB8) and Signed parallel halfword-wise subtraction (SSUB16) do update APSR.GE bits (for a complete list of instructions updating GE bits, see ARMv6 SIMD instruction intrinsics and APSR GE flags).
I will detail things on 16-bit data: if we consider one register holding two 16-bits samples (xk and xk+1) and one register holding two previous 16-bits maximum (maxeven and maxodd):
uint32_t max, data; max = (maxodd << 16) | (maxeven); data = (xk+1 << 16) | (xk);
Now we can parallel compare them by performing a parallel 16-bit subtraction, this will update GE bits as following:
(void)__SSUB16(max, data); /* tmp1 = maxodd - xk+1 ; GE[3:2] = (tmp1 >= 0)? 0b11 : 0b00 * tmp0 = maxeven - xk ; GE[1:0] = (tmp0 >= 0)? 0b11 : 0b00 */
Finally, we have only to keep maximum value on each halfword using SEL:
max = __SEL(max, data); /* maxodd = (GE[3:2] == 0b11)? maxodd : xk+1 * maxeven = (GE[1:0] == 0b00)? maxeven : xk */
For minimum detection, it’s almost the same thing :
uint32_t min, data; min = (minodd << 16) | (mineven); data = (xk+1 << 16) | (xk); (void)__SSUB16(data, min); /* tmp1 = xk+1 - minodd ; GE[3:2] = (tmp1 >= 0)? 0b11 : 0b00 * tmp0 = xk - mineven ; GE[1:0] = (tmp0 >= 0)? 0b11 : 0b00 */ min = __SEL(min, data); /* minodd = (GE[3:2] == 0b11)? minodd : xk+1 * mineven = (GE[1:0] == 0b00)? mineven : xk */
16-bits DSP implementation
Using previous logic to implement same Min/Max detection algorithm, we need to unroll the loop to perform 32-bit memory accesses. We also need to extract a single max and min value: I chose to do this outside the loop.
My 16-bit implementation is :
Implementation for 16-bits buffers
/* Using CMSIS DSP Library header for compiler abstraction */ #include "arm_math.h" uint32_t SearchMinMax16_DSP(int16_t* pSrc, int32_t pSize) { uint32_t data, min, max; int16_t data16; /* max variable will hold two max : one on each 16-bits half * same thing for min */ /* Load two first samples in one 32-bit access */ data = *__SIMD32(pSrc)++; /* Initialize Min and Max to these first samples */ min = data; max = data; /* decrement sample count */ pSize-=2; /* Loop as long as there remains at least two samples */ while (pSize > 1) { /* Load next two samples in a single access */ data = *__SIMD32(pSrc)++; /* Parallel comparison of max and new samples */ (void)__SSUB16(max, data); /* Select max on each 16-bits half */ max = __SEL(max, data); /* Parallel comparison of new samples and min */ (void)__SSUB16(data, min); /* Select min on each 16-bits half */ min = __SEL(min, data); pSize-=2; } /* Now we have maximum on even samples on low halfword of max * and maximum on odd samples on high halfword */ /* look for max between halfwords 1 & 0 by comparing on low halfword */ (void)__SSUB16(max, max >> 16); /* Select max on low 16-bits */ max = __SEL(max, max >> 16); /* look for min between halfwords 1 & 0 by comparing on low halfword */ (void)__SSUB16(min >> 16, min); /* Select min on low 16-bits */ min = __SEL(min, min >> 16); /* Test if odd number of samples */ if (pSize > 0) { data16 = *pSrc; /* look for max between on low halfwords */ (void)__SSUB16(max, data16); /* Select max on low 16-bits */ max = __SEL(max, data16); /* look for min on low halfword */ (void)__SSUB16(data16, min); /* Select min on low 16-bits */ min = __SEL(min, data16); } /* Pack result : Min on Low halfword, Max on High halfword */ return __PKHBT(min, max, 16); /* PKHBT documentation */ }
This implementation leads to following assembly listing (with IAR 7.30.4.8187 evaluation compiler but we would have similar output with Keil):
DSP 16 Optimized compiler output (-Oh)
; Bytes Cycles Comment SearchMinMax16_DSP: ; - 3 Function call PUSH {r4, r5} ; 2 3 Backup two registers LDR r2, [r0], #0x4 ; 4 2 Load 2 samples and post-increment SUBS r1, r1, #2 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter CMP r1, #1 ; 2 1 Test if we need to loop MOV r3, r2 ; 2 1 Copy loaded data to Min register MOV r4, r2 ; 2 1 Copy loaded data to Max register BLT final ; 2 1,3 Go through (1 cycle) or loop (3 cycles) loop: LDR r2, [r0], #0x4 ; 4 2 Load next 2 samples and post-increment SSUB16 r5, r4, r2 ; 4 1 Parallel compare Max to new samples ; GE[3:2]=((MaxH - SampleH) >= 0) ; GE[1:0]=((MaxL - SampleL) >= 0) SEL r4, r4, r2 ; 4 1 Keep Max on each halfword SUBS r1, r1, #2 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter SSUB16 r5, r2, r3 ; 4 1 Parallel compare new samples to Min ; GE[3:2]=((SampleH - MinH) >= 0) ; GE[1:0]=((SampleL - MinL) >= 0) CMP r1, #2 ; 2 1 Test remaining count SEL r3, r3, r2 ; 4 1 Keep Min on each halfword BGE loop ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) final: LSRS r2, r4, #16 ; 2 1 Put MaxH on low halfword SSUB16 r5, r4, r2 ; 4 1 Compare MaxL to MaxH ; GE[1:0]=((MaxL - MaxH) >= 0) SEL r2, r4, r2 ; 4 1 Keep Max on low halfword LSRS r4, r3, #16 ; 2 1 Put MinH on low halfword SSUB16 r5, r4, r3 ; 4 1 Compare MinL to MinH ; GE[1:0]=((MinL - MinH) >= 0) CMP r1, #1 ; 2 1 Test if sample count was odd SEL r3, r3, r4 ; 4 1 Keep Min on low halfword BLT finish ; 2 3,1 Skip (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) LDRSH r0, [r0] ; 4 2 Load last sample SSUB16 r1, r2, r0 ; 4 1 Compare Max to new sample ; GE[1:0]=((Max - sample) >= 0) SEL r2, r2, r0 ; 4 1 Keep Max on low halfword SSUB16 r1, r0, r3 ; 4 1 Compare new sample to Min ; GE[1:0]=((sample - Min) >= 0) SEL r3, r3, r0 ; 4 1 Keep Min on low halfword finish: POP {r4, r5} ; 2 3 Restore two registers PKHBT r0, r3, r2, LSL #16 ; 4 1 Pack result : Min on Low halfword, Max on High halfword BX LR ; 2 3 Return ROM : 94 bytes Stack : 8 bytes Cycles : N even : 13 + 11 * (N/2 - 2) + 26 N odd : 13 + 11 * (N/2 - 2) + 30
16-bits comparison
If we compare ROM and stack usage as well as computation cycles, we get following table:
| Impl. | max ROM | max Stack | Cycle Formula (N even) | 8 sps | 100 sps |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 42 bytes | 0 bytes | 9 + 12 * (N-2) + 15 | 96 cycles | 1200 cycles |
| DSP16 | 94 bytes | 8 bytes | 13 + 11 * (N/2-2) + 26 | 61 cycles | 567 cycles |
On a range from 2 to 100 samples, following graph shows both C and DSP implementations cycle count.
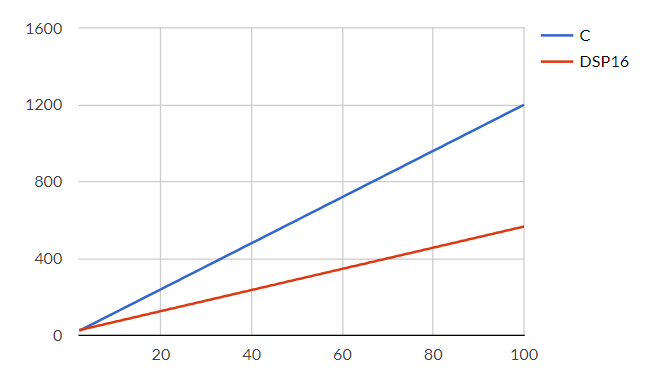
We have clearly enhanced efficiency on all cases (except when sample count is 2!).
In fact, C takes 12 cycles per sample no matter how many samples are treated where DSP implementation starts with 14 cycles per sample and tends to 5,5 for an infinite number of samples (and already under 6 cycles per sample when count > 32).
8-bits DSP implementation
If we make a comparable work on 8-bits data, this leads to a slightly more complex code since we need to unroll loop by 4 and then manage all remaining cases ():
Implementation for 8-bits buffers
#include "arm_math.h" /* Macro to perform post-incrementable 16-bits access */ #define __SIMD16(addr)(*(uint16_t **)&(addr)) #ifdef __ICCARM__ /* IAR is missing BFI (Bit Field Insert) intrinsic and does not automatically generate it where I would like to */ #pragma inline=forced static inline unsigned long __BFI(unsigned long base, unsigned long src, const unsigned char lsb, const unsigned char width) { unsigned long wRes = base; asm("BFI %0,%1,%2,%3" : "+r"(wRes) : "r"(src), "i"(lsb), "i"(width)); return wRes; } #endif uint16_t SearchMinMax8_DSP(int8_t* pSrc, int32_t pSize) { uint32_t data, min, max; /* max variable will hold four max : one on each byte * same thing for min */ /* Load four first samples in one 32-bit access */ data = *__SIMD32(pSrc)++; /* Initialize Min and Max to these first samples */ min = data; max = data; /* decrement sample count */ pSize -= 4; /* Loop as long as there remains at least four samples */ while (pSize >= 4) { /* Load next four samples in a single access */ data = *__SIMD32(pSrc)++; /* Parallel comparison of max and new samples */ (void)__SSUB8(max, data); /* Select max on each byte */ max = __SEL(max, data); /* Parallel comparison of new samples and min */ (void)__SSUB8(data, min); /* Select min on each byte */ min = __SEL(min, data); /* decrement sample count */ pSize -= 4; } /* Now we need to compare bytes in word to extract two max out of four */ /* look for max between bytes 3 & 1 and 2 & 0 */ (void)__SSUB8(max, max >> 16); /* Select max on bytes 1 & 0 */ max = __SEL(max, max >> 16); /* look for min between bytes 3 & 1 and 2 & 0 */ (void)__SSUB8(min >> 16, min); /* Select min on bytes 1 & 0 */ min = __SEL(min, min >> 16); /* Test if at least 2 samples remain */ if (pSize >= 2) { /* Load next two samples in a single access, only bytes 0 & 1 are interesting */ data = *__SIMD16(pSrc)++; /* Parallel comparison of max and new samples */ (void)__SSUB8(max, data); /* Select max on each byte */ max = __SEL(max, data); /* Parallel comparison of new samples and min */ (void)__SSUB8(data, min); /* Select min on each byte */ min = __SEL(min, data); /* decrement sample count */ pSize -= 2; } /* Now we need to compare bytes in low halfword to extract one max out of two */ /* look for max between bytes 1 & 0 */ (void)__SSUB8(max, max >> 8); /* Select max on byte 0 */ max = __SEL(max, max >> 8); /* look for min between bytes 1 & 0 */ (void)__SSUB8(min >> 8, min); /* Select min on byte 0 */ min = __SEL(min, min >> 8); /* Test if at least 1 sample remains */ if (pSize > 0) { /* Load last sample */ data = (uint32_t)*pSrc; /* Comparison of max and new sample */ (void)__SSUB8(max, data); /* Select max on byte 0 */ max = __SEL(max, data); /* Comparison of new sample and min */ (void)__SSUB8(data, min); /* Select min on byte 0 */ min = __SEL(min, data); } /* Pack result : Min on Byte 0, Max on Byte 1 */ #ifdef __ICCARM__ return __BFI(min, (uint8_t)max, 8, 24); #else return (uint16_t)((uint8_t)min | ((uint16_t)((uint8_t)max) << 8)); #endif }
After compilation (with IAR 7.30.4.8187 evaluation compiler), we get:
DSP 8 Optimized compiler output (-Oh)
; Bytes Cycles Comment SearchMinMax8_DSP: ; - 3 Function call PUSH {r4, r5} ; 2 3 Backup two registers LDR r3, [r0], #0x4 ; 4 2 Load 4 samples and post-increment SUBS r2, r1, #4 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter CMP r2, #4 ; 2 1 Test if we need to loop MOV r4, r2 ; 2 1 Copy loaded data to Min register MOV r5, r2 ; 2 1 Copy loaded data to Max register BCC step1 ; 2 1,3 Go through (1 cycle) or loop (3 cycles) loop: LDR r3, [r0], #0x4 ; 4 2 Load next 4 samples and post-increment SSUB8 r1, r5, r3 ; 4 1 Parallel compare Max to new samples ; GE[3]=((Max3 - Sample3) >= 0) ; GE[2]=((Max2 - Sample2) >= 0) ; GE[1]=((Max1 - Sample1) >= 0) ; GE[0]=((Max0 - Sample0) >= 0) SEL r5, r5, r3 ; 4 1 Keep max on each byte SUBS r2, r2, #4 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter SSUB8 r1, r3, r4 ; 4 1 Parallel compare new samples to Min ; GE[3]=((Sample3 - Min3) >= 0) ; GE[2]=((Sample2 - Min2) >= 0) ; GE[1]=((Sample1 - Min1) >= 0) ; GE[0]=((Sample0 - Min0) >= 0) CMP r2, #4 ; 2 1 Test remaining count SEL r4, r4, r3 ; 4 1 Keep Min on each byte BCS loop ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) step1: ; Compare Byte3 with Byte1 and Byte2 with Byte0 LSRS r1, r5, #16 ; 2 1 Put Max3,Max2 on low halfword SSUB8 r3, r5, r1 ; 4 1 Parallel compare Max1,Max0 to Max3,Max2 ; GE[1]=((Max1 - Max3) >= 0) ; GE[0]=((Max0 - Max2) >= 0) SEL r1, r5, r1 ; 4 1 Keep max on two lowest bytes LSRS r3, r4, #16 ; 2 1 Put Min3,Min2 on low halfword SSUB8 r5, r3, r4 ; 4 1 Parallel compare Min3,Min2 to Min1,Min0 ; GE[1]=((Min3 - Min1) >= 0) ; GE[0]=((Min2 - Min0) >= 0) CMP r2, #2 ; 2 1 Test if remaining sample count is at least 2 SEL r4, r4, r3 ; 4 1 Keep min on two lowest bytes BCC step2 ; 2 3,1 Skip (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) LDRH r3, [r0], #0x2 ; 4 2 Load two samples and post-increment SSUB8 r5, r1, r3 ; 4 1 Compare them to max (only lower 2 bytes) SEL r1, r1, r3 ; 4 1 Keep maximum SSUB8 r5, r3, r4 ; 4 1 Compare them to min (only lower 2 bytes) SEL r4, r4, r3 ; 4 1 Keep minimum SUBS r2, r2, #2 ; 2 1 Decrement sample count step2: ; Compare Byte1 with Byte0 LSRS r3, r1, #8 ; 2 1 Put Max1 on low byte SSUB8 r5, r1, r3 ; 4 1 Compare Max0 to Max1 ; GE[0]=((Max0 - Max1) >= 0) SEL r5, r1, r3 ; 4 1 Keep maximum on byte 0 LSRS r1, r4, #8 ; 2 1 Put Min1 on low byte SSUB8 r3, r1, r4 ; 4 1 Compare Min1 to Min0 ; GE[0]=((Min1 - Min0) >= 0) SEL r1, r4, r1 ; 4 1 Keep minimum on byte 0 CBZ r2, pack ; 2 3,1 Test one sample is remaining and branch on if not LDRSB r3, [r0] ; 4 2 Load last sample SSUB8 r0, r5, r3 ; 4 1 Compare max to new sample SEL r5, r5, r3 ; 4 1 Keep max on byte 0 SSUB8 r0, r3, r1 ; 4 1 Compare new sample to min SEL r1, r1, r3 ; 4 1 Keep min on byte 0 pack: ; Format data to be returned UXTB r5, r5 ; 2 1 Zero-extends 8-bit max to 32-bits BFI r1, r5, #8, #24 ; 4 1 Insert 24 lowest bits of max into 24 highest bits of min ; That puts min on byte0 and max on byte1 (and zeros on bytes 2 & 3) POP {r4, r5} ; 2 3 Restore two registers BX LR ; 2 3 Return ROM : 140 bytes Stack : 8 bytes Cycles : N % 4 = 0 : 13 + 11 * (N/4 - 2) + 36 N % 4 = 1 : 13 + 11 * (N/4 - 2) + 40 N % 4 = 2 : 13 + 11 * (N/4 - 2) + 41 N % 4 = 3 : 13 + 11 * (N/4 - 2) + 45
8-bits comparison
Comparing this output with C :
| Impl. | max ROM | max Stack | Cycle Formula (N multiple of 4) | 8 sps | 100 sps |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 40 bytes | 0 bytes | 9 + 12 * (N-2) + 15 | 96 cycles | 1200 cycles |
| DSP8 | 140 bytes | 8 bytes | 13 + 11 * (N/4-2) + 36 | 49 cycles | 302 cycles |
On a range from 4 to 100 samples, following graph shows both C and DSP implementations cycle count.

In 8-bits case, we can expect a division factor of 4 (Damn, this is the number of bytes we can treat in parallel!).
C still takes 12 cycles per sample no matter how many samples are treated where DSP implementation starts with 9,5 cycles per sample and tends to 2,75 for an infinite number of samples (already under 6 cycles per sample when count > 8, under 4 cycles when count > 21).
Going further
You can have a look at previous post which details a bit inlining. But bottom line is: if you have a fixed buffer size, fix the size in code! If you use this routine in a single place, allow your compiler to inline it!
This very same DSP 8-bit implementation now only takes 112 bytes of ROM and 38 cycles to detect min and max over 16 samples (compared to 71 without inlining, and 192 for C routine!).
