For this first post, we shall start simple and easy.
We will look into what I think is the simplest algorithm ever : averaging. You will see how much you can gain by looking hard at what your compiler does and what you could do to speed things up.
Constraints
In order to be able to compare to CMSIS, we will work with following constraints :
- Array of 16-bits samples, variable length limited to 65536
- Assuming array is 32-bits aligned
- No need to check pointer or size validity
- Result in 16-bits
Basic C approach
The algorithm consists in summing up all 16-bits samples in a 32-bit accumulator and divide by sample count at the end.
int16_t mean_C(int16_t* pSrc, uint32_t pSize) { int32_t sum = 0; uint32_t loop = pSize; while (loop-- > 0) { sum += *pSrc++; } return (int16_t)(sum / (int32_t)pSize); }
Now let’s have a look at compiler (Keil ARM Compiler V5.04.0.49 Evaluation) output with different Optimizations:
No Optimization (-O0); Bytes Cycles Comment mean_C: ; - 3 Function call PUSH {r4-r5,lr} ; 2 4 Backup MOV r2,r0 ; 2 1 Copy Array pointer to work register MOVS r3,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize accumulator MOV r4,r1 ; 2 1 Copy array size to work register B loop_mgmt ; 2 3 Always branch to end of loop loop_head: ; LDRSH r5,[r2],#0x02 ; 4 2 Load 16-bit sample and update pointer ADD r3,r3,r5 ; 2 1 Accumulate loop_mgmt: ; MOVS r0,r4 ; 2 1 Update Flags by moving remaining count SUB r4,r4,#0x01 ; 4 1 Decrement loop counter BNE loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) SDIV r0,r3,r1 ; 4 2-12 Divide by pSize SXTH r0,r0 ; 2 1 Cast to 16-bit POP {r4-r5,pc} ; 2 6 Restore backed up registers and return ROM : 32 bytes Stack : 12 bytes Cycles : 16 + 8 * N + [9-19]Highly optimized for size (-O3)
; Bytes Cycles Comment mean_C: ; - 3 Function call PUSH {r4,lr} ; 2 3 Backup MOVS r2,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize sum to zero MOV r3,r1 ; 2 1 Initialize loop counter to pSize B loop_mgmt ; 2 3 Always jump to end of loop loop_head: LDRSH r4,[r0],#0x02 ; 4 2 Load 16-bit sample and update pointer ADD r2,r2,r4 ; 2 1 Accumulate loop_mgmt: SUBS r3,r3,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter BCS loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) SDIV r0,r2,r1 ; 4 2-12 Divide by pSize SXTH r0,r0 ; 2 1 Cast to 16-bit POP {r4,pc} ; 2 5 Restore backed up register and return ROM : 26 bytes Stack : 8 bytes Cycles : 13 + 7 * N + [8-18]Highly optimized for speed (-O3 -Otime –loop_optimization_level=0)
; Bytes Cycles Comment mean_C: ; - 3 Function call MOVS r2,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize accumulator SUBS r3,r1,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter and update flags BCC exit ; 2 1 Branch only if pSize is 0 loop_head: LDRSH r12,[r0],#0x02 ; 4 2 Load 16-bit sample and update pointer SUBS r3,r3,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter and update flags ADD r2,r2,r12 ; 2 1 Accumulate BCS loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) exit: SDIV r0,r2,r1 ; 4 2-12 Divide by pSize SXTH r0,r0 ; 2 1 Cast to 16-bit BX lr ; 2 3 Return ROM : 24 bytes Stack : 0 bytes Cycles : 6 + 7 * (N - 1) + 5 + [6-16]Highly optimized for speed (-O3 -Otime)
; Bytes Cycles Comment mean_C: ; - 3 Function call PUSH {r4} ; 2 2 Backup MOVS r3,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize sum to zero MOV r2,r1 ; 2 1 Initialize loop counter to pSize CMP r1,#0x80000000 ; 4 1 Verify that size is unsigned BCS size_guard ; 2 1,3 Jump to special case for negative counts CMP r1,#0x00 ; 2 1 Test if size is zero BLE end ; 2 1,3 Jump to end if size is zero (and divide by zero ....) SUBS r0,r0,#2 ; 2 1 Pre-decrement sample pointer TST r1,#0x01 ; 4 1 Test if size is odd IT NE ; 2 1 Execute following Load if size is odd ;(this load pre-increments sample pointer and writes back to it) LDRSHNE r3,[r0,#0x02]! ; 4 1,2 Conditionally initialize accumulator with this odd sample MOVS r4,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize second accumulator ASRS r12,r1,#1 ; 4 1 Divide size by 2 BEQ final_acc ; 2 1,3 Jump to end if nothing else to do (size was 1) loop_head: LDRSH r2,[r0,#0x02] ; 4 2 Load from pre-incremented sample pointer and don't update SUBS r12,r12,#0x01 ; 4 1 Decrement loop counter ADD r3,r3,r2 ; 2 1 Accumulate on first accumulator LDRSH r2,[r0,#0x04]! ; 4 2 Load from pre-incremented sample pointer and update it ADD r4,r4,r2 ; 2 1 Accumulate on second accumulator BNE loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) final_acc: ADD r3,r3,r4 ; 2 1 Accumulate both accumulators end_label: SDIV r0,r3,r1 ; 4 2-12 Divide by pSize POP {r4} ; 2 2 Restore backed up register SXTH r0,r0 ; 2 1 Cast to 16-bit BX lr ; 2 3 Return negative_size: LDRSH r12,[r0],#0x02 ; 4 2 Load from post-incremented sample pointer and update it SUBS r2,r2,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter ADD r3,r3,r12 ; 2 1 Accumulate BNE negative_size ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) B end_label ; 2 3 Final branch to end ROM : 78 bytes Stack : 4 bytes Cycles : N even >= 2 : 18 + (N/2 - 1) * 10 + 8 + [9-19] N odd >= 3 : 19 + (N/2 - 1) * 10 + 8 + [9-19]
Summary (division cycle count arbitrarily set to 7) :
| Opt level | ROM | Stack | Cycle Formula | 4 samples | 100 samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 32 bytes | 12 bytes | 30 + 8 * N | 62 cycles | 830 cycles |
| High size | 26 bytes | 8 bytes | 26 + 7 * N | 54 cycles | 726 cycles |
| High speed | 24 bytes | – | 17 + 7 * (N-1) + 5 | 43 cycles | 715 cycles |
| High speed w/ unroll | 78 bytes | 4 bytes | 18 + 10 * (N/2-1) + 22 | 50 cycles | 530 cycles |
Funny thing to notice is that optimizing for speed sometimes leads to better size optimization or seen another way, optimizing for speed is not necessarily greedy in ROM (main contributor to this greediness is loop unrolling).
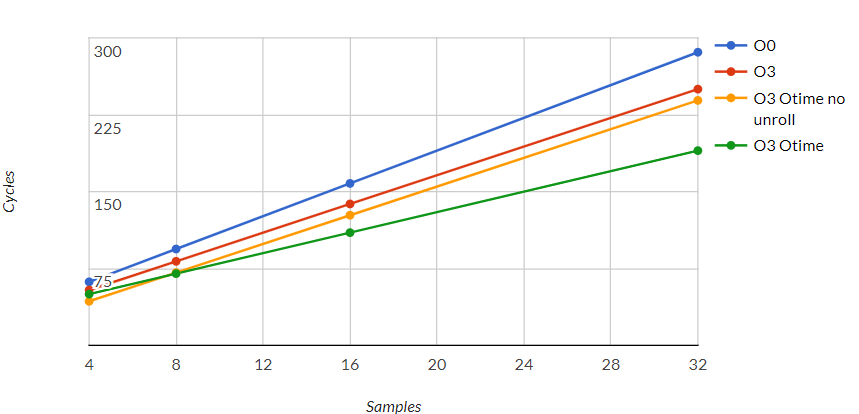
Also, what is interesting to notice (and what we will try to reduce) is the « cost » of loop compared to « useful » instructions and the weight of memory accesses (PUSH, POP, LDRSH). On top of that, if you’re working with big buffers, it is the loop content that you want to speed up and if you’re working with small ones, well the whole routine needs to improved.
Look at intrinsics
We can « see » that a Load costs 2 cycles where all arithmetic instructions cost 1. First idea is then to minimize number of loads. Loading 8, 16 or 32 bits costs the same thing so let’s load 32-bits at a time. A register will now hold two 16-bits samples and we need to accumulate them in another 32-bits variable.
Let’s have a look at ARM instruction set Cheat Sheet.
In Parallel arithmetic paragraph, nothing interesting since all of them (except USAD8 and USADA8) perform vector operation (data in Low and High halfword are not mixed).
In Sign extensions paragraph, there is an interesting one : SXTAH, it seems that this could extract one 16-bit signed value from either halfword of source and accumulate it to 32-bit. OK, this could do the trick but we would need two of these per 32-bit load.
Finally, in Multiply paragraph, we see many accumulations on parallel halfwords but it seems that we should multiply with something. SMUAD and SMLAD are the closest ones to what we try to do.
Before writing the updated C routine, we need to make sure that there are some intrinsics available. Usually, you can find them in your compiler documentation. I’ve always seen them written using two underscores in front in either case (depending on compiler):
__SXTAH or __SMLAD.
If you cannot find what you’re looking for, there is another way : inline assembly.
Since we use high level of optimization, we can write some inline assembly in a static inline routine that can be called just like any other function.
For instance, we want to use SXTAH with the rotation attribute but my compiler doesn’t have this one, here is what I would write for Keil:
__forceinline static int32_t __SXTAH_ROR16(uint32_t pair, int32_t acc) { int32_t res; __asm { SXTAH res, acc, pair, ROR #16 }; return res; }
and for GCC (or IAR)
__attribute__((always_inline)) static inline int32_t __SXTAH_ROR16(uint32_t pair, int32_t acc) { int32_t res; asm ( "SXTAH %0, %1, %2, ROR #16" : "=r"(res) : "r"(acc), "r"(pair)); return res; }
This leads to updated C routine
#define __SIMD32(addr)(*(uint32_t **)&(addr)) int16_t mean_SXTAH(int16_t* pSrc, uint32_t pSize) { int32_t sum = 0; uint32_t pair, loop = pSize >> 1; if (pSize & 0x1) { sum = *pSrc++; } while (loop-- > 0) { pair = *__SIMD32(pSrc)++; sum = __SXTAH(pair, sum); sum = __SXTAH_ROR16(pair, sum); } return (int16_t)(sum / (int32_t)pSize); }SMLAD unroll by 2
int16_t mean_SMLAD(int16_t* pSrc, uint32_t pSize) { int32_t sum = 0; uint32_t pair, loop = pSize >> 1; if (pSize & 0x1) { sum = *pSrc++; } while (loop-- > 0) { pair = *__SIMD32(pSrc)++; sum = __SMLAD(pair, 0x00010001u, sum); } return (int16_t)(sum / (int32_t)pSize); }SMLAD unroll by 4
int16_t mean_SMLAD2(int16_t* pSrc, uint32_t pSize) { int32_t sum = 0; uint32_t pair, loop = pSize >> 2; while (loop-- > 0) { pair = *__SIMD32(pSrc)++; sum = __SMLAD(pair, 0x00010001u, sum); pair = *__SIMD32(pSrc)++; sum = __SMLAD(pair, 0x00010001u, sum); } if (pSize & 0x2) { pair = *__SIMD32(pSrc)++; sum = __SMLAD(pair, 0x00010001u, sum); } if (pSize & 0x1) { sum+= *pSrc++; } return (int16_t)(sum / (int32_t)pSize); }
And CMSIS one …
/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------- * Copyright (C) 2010-2014 ARM Limited. All rights reserved. * * $Date: 12. March 2014 * $Revision: V1.4.3 * * Project: CMSIS DSP Library * Title: arm_mean_q15.c * * Description: Mean value of a Q15 vector. * * Target Processor: Cortex-M4/Cortex-M3/Cortex-M0 * * Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without * modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions * are met: * - Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. * - Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in * the documentation and/or other materials provided with the * distribution. * - Neither the name of ARM LIMITED nor the names of its contributors * may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this * software without specific prior written permission. * * THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS * "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT * LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS * FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE * COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, * INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, * BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; * LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER * CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT * LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN * ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE * POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. * -------------------------------------------------------------------- */ void arm_mean_q15( q15_t * pSrc, uint32_t blockSize, q15_t * pResult) { q31_t sum = 0; /* Temporary result storage */ uint32_t blkCnt; /* loop counter */ /* Run the below code for Cortex-M4 and Cortex-M3 */ q31_t in; /*loop Unrolling */ blkCnt = blockSize >> 2u; /* First part of the processing with loop unrolling. Compute 4 outputs at a time. ** a second loop below computes the remaining 1 to 3 samples. */ while(blkCnt > 0u) { /* C = (A[0] + A[1] + A[2] + ... + A[blockSize-1]) */ in = *__SIMD32(pSrc)++; sum += ((in << 16) >> 16); sum += (in >> 16); in = *__SIMD32(pSrc)++; sum += ((in << 16) >> 16); sum += (in >> 16); /* Decrement the loop counter */ blkCnt--; } /* If the blockSize is not a multiple of 4, compute any remaining output samples here. ** No loop unrolling is used. */ blkCnt = blockSize % 0x4u; while(blkCnt > 0u) { /* C = (A[0] + A[1] + A[2] + ... + A[blockSize-1]) */ sum += *pSrc++; /* Decrement the loop counter */ blkCnt--; } /* C = (A[0] + A[1] + A[2] + ... + A[blockSize-1]) / blockSize */ /* Store the result to the destination */ *pResult = (q15_t) (sum / (q31_t)blockSize); }
If you look at what this generates (with high optimization for speed enabled) we have:
SXTAH unroll by 2; Bytes Cycles Comment mean_SXTAH: ; - 3 Function call MOVS r2,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize sum to zero LSRS r3,r1,#1 ; 2 1 Divide size by 2 TST r1,#0x01 ; 4 1 Test if size is odd IT NE ; 2 1 Execute following Load if size is odd LDRSHNE r2,[r0],#0x02 ; 4 1,2 Conditionally initialize accumulator with this odd sample SUBS r12,r3,#1 ; 4 1 Decrement loop counter BCC end_label ; 2 1,3 Jump to end if size was 0 or 1 loop_head: LDR r3,[r0],#0x04 ; 4 2 Load 32-bits and post-increment SXTAH r2,r2,r3 ; 4 1 Extract Low Halfword and accumulate it SXTAH r2,r2,r3,ROR #16 ; 4 1 Extract High Halfword and accumulate it SUBS r12,r12,#1 ; 4 1 Decrement loop counter BCS loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) end_label: SDIV r0,r2,r1 ; 4 2-12 Divide by pSize SXTH r0,r0 ; 2 1 Cast to 16-bit BX lr ; 2 3 Return ROM : 46 bytes Stack : 0 bytes Cycles : N even >= 2 : 10 + (N/2 - 1) * 8 + 6 + [6-16] N odd >= 3 : 11 + (N/2 - 1) * 8 + 6 + [6-16]SMLAD unroll by 2
; Bytes Cycles Comment mean_SMLAD: ; - 3 Function call PUSH {r4} ; 2 2 Backup MOVS r2,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize sum to zero LSRS r3,r1,#1 ; 2 1 Initialize loop counter to pSize/2 TST r1,#0x01 ; 4 1 Test if size is odd IT NE ; 2 1 Execute following Load if size is odd LDRSHNE r2,[r0],#0x02 ; 4 1,2 Conditionally initialize accumulator with this odd sample SUBS r3,r3,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter IT CS ; 2 1 Execute following MOV if size was > 1 MOVCS r4,#0x10001 ; 4 1 Initialize constant coefficients BCC end_label ; 2 1,3 Jump to end if size was 0 or 1 NOP ; 2 0,1 Padding instruction, "may not take 1 cycle" loop_head: LDR r12,[r0],#0x04 ; 4 2 Load 32-bits and post-increment SMLAD r2,r12,r4,r2 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply both samples by 1 and accumulate SUBS r3,r3,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter BCS loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) end_label: SDIV r0,r2,r1 ; 4 2-12 Divide by pSize POP {r4} ; 2 2 Restore backed up register SXTH r0,r0 ; 2 1 Cast to 16-bit BX lr ; 2 3 Return ROM : 50 bytes Stack : 4 bytes Cycles : N even >= 2 : 14 + (N/2 - 1) * 7 + 5 + [8-18] N odd >= 3 : 15 + (N/2 - 1) * 7 + 5 + [8-18]SMLAD unroll by 4
; Bytes Cycles Comment mean_SMLAD2: ; - 3 Function call PUSH {r4} ; 2 2 Backup MOVS r2,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize sum to zero LSRS r4,r1,#2 ; 2 1 Initialize loop counter to pSize/4 SUBS r12,r4,#0x01 ; 4 1 Decrement loop counter MOV r3,#0x10001 ; 4 1 Initialize constant coefficients BCC final_adjust2 ; 2 1,3 Jump to final adjustments if size was < 4 loop_head: LDR r4,[r0],#0x04 ; 4 2 Load 32-bits and post-increment SMLAD r2,r4,r3,r2 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply both samples by 1 and accumulate LDR r4,[r0],#0x04 ; 4 2 Load 32-bits and post-increment SMLAD r2,r4,r3,r2 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply both samples by 1 and accumulate SUBS r12,r12,#0x01 ; 4 1 Decrement loop counter BCS loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) final_adjust2: TST r1,#0x02 ; 4 1 Test if size remainder is >= 2 BEQ final_adjust1 ; 2 1,3 Jump to last adjustments if size remainder was < 2 LDR r12,[r0],#0x04 ; 4 2 Load 32-bits and post-increment SMLAD r2,r12,r3,r2 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply both samples by 1 and accumulate final_adjust1: TST r1,#0x01 ; 4 1 Test if size is odd ITT NE ; 2 1 Execute following Load and Add if size is odd LDRSHNE r0,[r0,#0x00] ; 4 1,2 Conditionally load this odd sample ADDNE r2,r2,r0 ; 2 1 Conditionally accumulate it SDIV r0,r2,r1 ; 4 2-12 Divide by pSize POP {r4} ; 2 2 Restore backed up register SXTH r0,r0 ; 2 1 Cast to 16-bit BX lr ; 2 3 Return ROM : 74 bytes Stack : 4 bytes Cycles : N multiple of 4 : 10 + (N/4 - 1) * 10 + 8 + 8 + [8-18] N m*4 + 3 >= 7 : 10 + (N/4 - 1) * 10 + 8 + 10 + [8-18] N m*4 + 2 >= 6 : 10 + (N/4 - 1) * 10 + 8 + 9 + [8-18] N m*4 + 1 >= 5 : 10 + (N/4 - 1) * 10 + 8 + 9 + [8-18]Also looking at CMSIS output, we can notice that compiler had a weird behavior: following listing is the original one, next one is what I would expect from written C code (and what I think an ideal compiler would output) CMSIS arm_mean_q15 v1.4.3 Keil library This assembly listing is the very output of a disassembly of provided arm_cortexM4l_math.lib included in uVision 5 CMSIS 4.1.0 Pack. Compiling the previous source code with -O3 -Otime options outputs the same assembler.
; Copyright (C) 2009-2012 ARM Limited. ; All rights reserved. ; ; Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without ; modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met: ; - Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright ; notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. ; - Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright ; notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the ; documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution. ; - Neither the name of ARM nor the names of its contributors may be used ; to endorse or promote products derived from this software without ; specific prior written permission. ; ; THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" ; AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE ; IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ; ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS BE ; LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR ; CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF ; SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS ; INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN ; CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ; ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE ; POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. ; Bytes Cycles Comment arm_mean_q15: ; - 3 Function call PUSH {r4-r8} ; 4 6 Backup MOVS r3,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize sum to zero LSR r12,r1,#2 ; 4 1 Initialize loop count to pSize/4 CMP r12,#0x80000000 ; 4 1 Verify that shifted size is unsigned ;(always the case since we LOGICAL shifted just before) BCS size_guard ; 2 1,3 Jump to special case for negative counts (never taken) MOVS r4,#0x01 ; 2 1 Initialize loop counter to 1 ADD r5,r12,#0x01 ; 4 1 Prepare maximum loop counter (loop count + 1) CMP r5,#0x01 ; 2 1 Loop comparison BLE final_adjust3 ; 2 1,3 Skip the loop if loop count was 0 NOP ; 2 0,1 Padding instruction, "may not take 1 cycle" loop_head: LDR r12,[r0],#0x04 ; 4 2 Load 32-bits and post-increment SXTAH r3,r3,r12 ; 4 1 Extract Low Halfword and accumulate it ADD r12,r3,r12,ASR #16 ; 4 1 Extract High Halfword and accumulate it LDR r3,[r0],#0x04 ; 4 2 Load 32-bits and post-increment SXTAH r12,r12,r3 ; 4 1 Extract Low Halfword and accumulate it ADDS r4,r4,#1 ; 2 1 Increment loop counter ADD r3,r12,r3,ASR #16 ; 4 1 Extract High Halfword and accumulate it CMP r5,r4 ; 2 1 Compare loop counter to loop count BGT loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) final_adjust3: AND r12,r1,#0x03 ; 4 1 Extract last 2 bits of pSize CMP r12,#0x80000000 ; 4 1 Verify that it is unsigned ... BCS size_guard2 ; 2 1,3 Jump to special case for negative counts (never taken) SUB r5,r12,#0x01 ; 4 1 Compute if remaining size - 1 CMP r5,#0x00 ; 2 1 Check if remaining size - 1 is zero BLE final_adjust1 ; 2 1,3 Jump to last adjustment (for remaining size = 1 or 0) SUBS r4,r0,#2 ; 2 1 Go one sample backward (pointer update) TST r12,#0x01 ; 4 1 Test if remaining size is odd BNE final_adjust3b ; 2 1,3 LDRSH r6,[r4,#0x02]! ; 4 2 ADD r3,r3,r6 ; 2 1 Tired of commenting all this ... final_adjust3b: LDRSH r7,[r4,#0x02] ; 4 2 MOVS r6,#0x00 ; 2 1 ASRS r5,r5,#1 ; 2 1 BEQ final_adjust1 ; 2 1,3 final_adjust2: LDRSH r8,[r4,#0x04]! ; 4 2 ADD r3,r3,r7 ; 2 1 LDRSH r7,[r4,#0x02] ; 4 2 ADD r6,r6,r8 ; 2 1 SUBS r5,r5,#1 ; 2 1 BNE final_adjust2 ; 2 1,3 ADD r3,r3,r6 ; 2 1 final_adjust1: SUBS r12,r12,#0x01 ; 4 1 Decrement remaining size ITT PL ; 2 1 Execute following Load & acc if size was 1 LDRSHPL r0,[r0,r12,LSL #1] ; 4 2,1 Conditionally load final sample ADDPL r3,r3,r0 ; 2 1 Conditionally accumulate it end_label: SDIV r0,r3,r1 ; 4 2-12 Divide by pSize STRH r0,[r2,#0x00] ; 2 2 Write result at address pointed by pResult POP {r4-r8} ; 4 6 Restore backed up registers BX lr ; 4 3 Return size_guard: LDR r4,[r0],#0x04 ; 4 2 SXTAH r3,r3,r4 ; 4 1 ADD r4,r3,r4,ASR #16 ; 4 1 LDR r3,[r0],#0x04 ; 4 2 SXTAH r4,r4,r3 ; 4 1 ADD r3,r4,r3,ASR #16 ; 4 1 SUBS r12,r12,#0x01 ; 4 1 BNE size_guard ; 2 3,1 B final_adjust3 ; 2 3 size_guard2: LDRSH r4,[r0],#0x02 ; 4 2 SUBS r12,r12,#0x01 ; 4 1 ADD r3,r3,r4 ; 2 1 BNE size_guard ; 2 3,1 B end_label ; 2 3 ROM : 190 bytes Stack : 20 bytes Cycles : N multiple of 4 : 17 + (N/4 - 1) * 13 + 11 + 12 + [13-23] Other cases : moreCMSIS arm_mean_q15 v1.4.3 (what could be expected)
; Bytes Cycles Comment arm_mean_q15: ; - 3 Function call PUSH {r4} ; 2 2 Backup r4 MOVS r3, #0 ; 2 1 Initialize sum to zero LSRS r4, r1, #2 ; 2 1 Initialize loop count to pSize/4 test if new size is zero BEQ final_adjust ; 2 1,3 Skip the loop if loop count was 0 main_loop_head: LDR r12, [r0], #0x4 ; 4 2 Load 32-bits and post-increment SXTAH r3, r3, r12 ; 4 1 Extract Low Halfword and accumulate it ADD r3, r3, r12, ASR #16 ; 4 1 Extract High Halfword and accumulate it LDR r12, [r0], #0x4 ; 4 2 Load 32-bits and post-increment SXTAH r3, r3, r12 ; 4 1 Extract Low Halfword and accumulate it SUBS r4, r4, #1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter & update flags ADD r3, r3, r12, ASR #16 ; 4 1 Extract High Halfword and accumulate it BNE main_loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) final_adjust: TST r1, #3 ; 4 1 Test if size remainder is 0 BEQ end_label ; 4 1,3 Jump to final division if initial size was multiple of 4 AND r4, r1, #3 ; 4 1 Keep only last 2 bits of pSize final_loop_head: LDRSH r12, [r0], #0x2 ; 4 2 Load 16-bits and post-increment ADD r3, r3, r12 ; 4 1 Accumulate SUBS r4, r4, #1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter & update flags BNE final_loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) end_label: SDIV r0, r3, r1 ; 4 2-12 Divide by pSize STRH r0, [r2] ; 2 2 Write result at address pointed by pResult POP {r4} ; 2 2 Restore backed up register BX LR ; 2 3 Return ROM : 70 bytes Stack : 4 bytes Cycles : N multiple of 4 : 9 + (N/4 - 1) * 12 + 10 + 4 + [10-20] N m*4 + 3 >= 7 : 9 + (N/4 - 1) * 12 + 10 + 3 + 2 * 7 + 5 + [10-20] N m*4 + 2 >= 6 : 9 + (N/4 - 1) * 12 + 10 + 3 + 1 * 7 + 5 + [10-20] N m*4 + 1 >= 5 : 9 + (N/4 - 1) * 12 + 10 + 3 + 0 * 7 + 5 + [10-20]
Summary (division cycle count arbitrarily set to 7) :
| Implementation | ROM | Stack | Cycle Formula (multiple of 4) | 4 samples | 100 samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean_SXTAH | 46 bytes | 0 bytes | 10 + 8 * (N/2-1) + 17 | 35 cycles | 419 cycles |
| mean_SMLAD | 50 bytes | 4 bytes | 14 + 7 * (N/2-1) + 18 | 39 cycles | 375 cycles |
| mean_SMLAD2 | 74 bytes | 4 bytes | 10 + 10 * (N/4-1) + 29 | 39 cycles | 279 cycles |
| arm_mean_q15 (Keil) | 190 bytes | 20 bytes | 17 + 13 * (N/4-1) + 41 | 58 cycles | 370 cycles |
| arm_mean_q15 (ideal) | 70 bytes | 4 bytes | 9 + 12 * (N/4-1) + 29 | 38 cycles | 326 cycles |

So here, we are at a point of optimization where we are comparable to CMSIS, at least the intended effort of CMSIS developers. We see that this allows to speed processing of this very simple algorithm, especially for big buffers.
If you have variable sizes in your application or want to manage all cases, this is where optimization should end.
Important note:
- You may have noticed that the CMSIS arm_mean_q15 routine is written in pure C without the use of M4 intrinsics. Well, that’s a shame, SMLAD shows that this could help to speed things up even more.
- It is not because you got an « optimized » library that its content is really optimized: the previously listed disassembly shows 120 bytes ROM, 16 stack bytes and a minimum of 20 cycles lost because of compiler compared to what was intended.
Going further
So now, what we can extract from all this work is being optimal for every case is not possible, we have to make choices between low overhead (for small buffers), or effective loop content and deal with special cases (negative length, odd counts …).
I will not tell you to write a specific routine for all your possible cases, that’s not realistic! What I suggest is to let your compiler work by allowing it to do so:
If you write your algorithm in the same compilation unit as its usage and tell your compiler he can take shortcuts (basically telling it that only what it sees will use your routine), he will do great things!
In terms of C, I talk about static inline routines, potentially declared in header files with constant parameters.
Here are compiler (Keil) outputs for various buffer sizes (4, 13, 16 and 100) on a couple of previous implementations.
Still the same C routine;Buffer size = 4 LDRSH r1,[r0,#0x00] ; 4 2 Load from sample pointer and don't update LDRSH r2,[r0,#0x02] ; 4 2 Load from pre-incremented sample pointer and don't update ADD r1,r1,r2 ; 2 1 Accumulate LDRSH r2,[r0,#0x04] ; 4 2 Load from pre-incremented sample pointer and don't update LDRSH r0,[r0,#0x06] ; 4 2 Load from pre-incremented sample pointer and don't update ADD r1,r1,r2 ; 2 1 Accumulate ADD r0,r0,r1 ; 2 1 Accumulate ; Following 3 instructions emulate division behaviour : div rounds towards 0 on positive and negative numbers ASRS r1,r0,#31 ; 2 1 Get result sign ADD r0,r0,r1,LSR #30 ; 4 1 Add 3 if result is negative (0.75 after following shift) ASRS r0,r0,#2 ; 2 1 Shift result by 2 ROM : 30 bytes Stack : 0 bytes Cycles : 14 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ;Buffer size = 13 MOVS r2,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize second accumulator to zero LDRSH r1,[r0,#0x00] ; 4 2 Load from sample pointer and don't update MOVS r3,#0x06 ; 4 1 Initialize loop counter to 6 loop_head: LDRSH r12,[r0,#0x02] ; 4 2 Load from pre-incremented sample pointer and don't update SUBS r3,r3,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter ADD r1,r1,r12 ; 2 1 Accumulate on first accumulator LDRSH r12,[r0,#0x04]! ; 4 2 Load from pre-incremented sample pointer and update it ADD r2,r2,r12 ; 2 1 Accumulate on second accumulator BNE loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) ADDS r0,r1,r2 ; 2 1 Merge both accumulators ; Following 4 instructions emulate division using multiplication with a constant LDR r1,[pc,#132] ; 2 2 Load division constant 0x4EC4EC4F (2^34 / 13) SMULL r1,r0,r1,r0 ; 4 1 Multiply result by the constant, result on 64 bits ASRS r1,r0,#2 ; 2 1 Divide Most significant word by 4 SUB r0,r1,r0,ASR #31 ; 4 1 Add 1 if result is negative ROM : 40 bytes Stack : 0 bytes Cycles : 68 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ;Buffer size = 16 MOVS r2,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize second accumulator to zero MOV r1,r2 ; 2 1 Copy Zero to first accumulator MOVS r3,#0x08 ; 2 1 Initialize loop counter to 8 loop_head: LDRSH r12,[r0,#0x02] ; 4 2 Load from pre-incremented sample pointer and don't update SUBS r3,r3,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter ADD r2,r2,r12 ; 2 1 Accumulate on second accumulator LDRSH r12,[r0,#0x04]! ; 4 2 Load from pre-incremented sample pointer and update it ADD r1,r1,r12 ; 2 1 Accumulate on first accumulator BNE loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) ADDS r0,r2,r1 ; 2 1 Merge both accumulators ; Following 3 instructions emulate division using shift operation ASRS r1,r0,#31 ; 2 1 Get result sign ADD r0,r0,r1,LSR #28 ; 4 1 Add 15 if result is negative (0.9375 after following shift) ASRS r0,r0,#4 ; 2 1 Shift result by 4 ROM : 32 bytes Stack : 0 bytes Cycles : N = 16 : 85 N power of 2 : 3 + (N/2 - 1) * 10 + 8 + 3 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ;Buffer size = 100 MOVS r2,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize second accumulator to zero MOV r1,r2 ; 2 1 Copy Zero to first accumulator MOVS r3,#0x32 ; 2 1 Initialize loop counter to 50 loop_head: LDRSH r12,[r0,#0x02] ; 4 2 Load from pre-incremented sample pointer and don't update SUBS r3,r3,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter ADD r2,r2,r12 ; 2 1 Accumulate on second accumulator LDRSH r12,[r0,#0x04]! ; 4 2 Load from pre-incremented sample pointer and update it ADD r1,r1,r12 ; 2 1 Accumulate on first accumulator BNE loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) ADDS r0,r2,r1 ; 2 1 Merge both accumulators LDR r1,[pc,#48] ; 2 2 Load division constant 0x51EB851F (2^37 / 100) SMULL r1,r0,r1,r0 ; 4 1 Multiply result by the constant, result on 64 bits ASRS r1,r0,#5 ; 2 1 Divide Most significant word by 32 SUB r0,r1,r0,ASR #31 ; 4 1 Add 1 if result is negative ROM : 36 bytes Stack : 0 bytes Cycles : N = 100 : 507 N even (not a power of 2) : 3 + (N/2 - 1) * 10 + 8 + 6Still the same SMLAD unroll by 4 routine
;Buffer size = 4 MOVS r1,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize accumulator to zero LDR r3,[r0,#0x00] ; 2 2 Load 32-bits and don't update MOV r2,#0x10001 ; 4 1 Initialize constant coefficients SMLAD r1,r3,r2,r1 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply both samples by 1 and accumulate LDR r0,[r0,#0x04] ; 2 2 Load next 32-bits and don't update SMLAD r0,r0,r2,r1 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply both samples by 1 and accumulate ; Following 3 instructions emulate division behaviour : div rounds towards 0 on positive and negative numbers ASRS r1,r0,#31 ; 2 1 Get result sign ADD r0,r0,r1,LSR #30 ; 4 1 Add 3 if result is negative (0.75 after following shift) ASRS r0,r0,#2 ; 2 1 Shift result by 2 ROM : 26 bytes Stack : 0 bytes Cycles : 11 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ;Buffer size = 13 MOVS r1,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize accumulator to zero MOVS r2,#0x02 ; 2 1 Initialize loop counter to 2 MOV r3,#0x10001 ; 4 1 Initialize constant coefficients NOP ; 2 0,1 Padding instruction, "may not take 1 cycle" loop_head: LDR r12,[r0],#0x04 ; 4 2 Load 32-bits and post-increment SMLAD r1,r12,r3,r1 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply both samples by 1 and accumulate LDR r12,[r0],#0x04 ; 4 2 Load 32-bits and post-increment SMLAD r1,r12,r3,r1 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply both samples by 1 and accumulate SUBS r2,r2,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter and update flags BCS loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) LDRSH r0,[r0,#0x00] ; 4 2 Load final 16-bits and don't update ADD r0,r0,r1 ; 2 1 Accumulate it ; Following 4 instructions emulate division using multiplication with a constant LDR r1,[pc,#144] ; 2 2 Load division constant 0x4EC4EC4F (2^34 / 13) SMULL r1,r0,r1,r0 ; 4 1 Multiply result by the constant, result on 64 bits ASRS r1,r0,#2 ; 2 1 Divide Most significant word by 4 SUB r0,r1,r0,ASR #31 ; 4 1 Add 1 if result is negative ROM : 48 bytes Stack : 0 bytes Cycles : 39 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ;Buffer size = 16 MOVS r1,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize accumulator to zero MOVS r2,#0x03 ; 2 1 Initialize loop counter to 3 MOV r3,#0x10001 ; 4 1 Initialize constant coefficients NOP ; 2 0,1 Padding instruction, "may not take 1 cycle" loop_head: LDR r12,[r0],#0x04 ; 4 2 Load 32-bits and post-increment SMLAD r1,r12,r3,r1 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply both samples by 1 and accumulate LDR r12,[r0],#0x04 ; 4 2 Load 32-bits and post-increment SMLAD r1,r12,r3,r1 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply both samples by 1 and accumulate SUBS r2,r2,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter and update flags BCS loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) ; Following 3 instructions emulate division using shift operation ASRS r0,r1,#31 ; 2 1 Get result sign ADD r0,r1,r0,LSR #28 ; 4 1 Add 15 if result is negative (0.9375 after following shift) ASRS r0,r0,#4 ; 2 1 Shift result by 4 ROM : 38 bytes Stack : 0 bytes Cycles : N = 16 : 44 N power of 2 : 3 + (N/4 - 1) * 10 + 8 + 3 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ;Buffer size = 100 MOVS r2,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize accumulator to zero MOVS r1,#0x18 ; 2 1 Initialize loop counter to 24 MOV r3,#0x10001 ; 4 1 Initialize constant coefficients loop_head: LDR r12,[r0],#0x04 ; 4 2 Load 32-bits and post-increment SMLAD r2,r12,r3,r2 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply both samples by 1 and accumulate LDR r12,[r0],#0x04 ; 4 2 Load 32-bits and post-increment SMLAD r2,r12,r3,r2 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply both samples by 1 and accumulate SUBS r1,r1,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter and update flags BCS loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) ; Following 4 instructions emulate division using multiplication with a constant LDR r0,[pc,#44] ; 2 2 Load division constant 0x51EB851F (2^37 / 100) SMULL r1,r0,r0,r2 ; 4 1 Multiply result by the constant, result on 64 bits ASRS r1,r0,#5 ; 2 1 Divide Most significant word by 32 SUB r0,r1,r0,ASR #31 ; 4 1 Add 1 if result is negative ROM : 40 bytes Stack : 0 bytes Cycles : 256
Looking at these results, we can see that all unnecessary tests are stripped, so why not write some more C code to have less assembly …
More C, less cycles ! Final implementationtypedef union { struct { uint32_t LSW; /* Least significant Word */ uint32_t MSW; /* Most significant Word */ }regs; uint64_t pair; }RegPair_t; #define __SIMD32(addr)(*(uint32_t **)&(addr)) #define __SIMD64(addr)(*(uint64_t **)&(addr)) __forceinline static int16_t mean_SMLAD3(int16_t* pSrc, uint32_t pSize) { int32_t sum; RegPair_t big; uint32_t pair, loop = pSize >> 3; /* Initialize loop to pSize / 8 */ if (loop > 0) { /* Only for big loops (pSize >= 8) */ big.pair = *__SIMD64(pSrc)++; /* Load 64 bits => 4 samples */ /* Special case, initialize accumulator */ sum = __SMUAD(big.regs.LSW, 0x00010001u); sum = __SMLAD(big.regs.MSW, 0x00010001u, sum); big.pair = *__SIMD64(pSrc)++; sum = __SMLAD(big.regs.LSW, 0x00010001u, sum); sum = __SMLAD(big.regs.MSW, 0x00010001u, sum); loop--; while (loop-- > 0) { /* loop on remaining 128 bits (8 samples) */ big.pair = *__SIMD64(pSrc)++; sum = __SMLAD(big.regs.LSW, 0x00010001u, sum); sum = __SMLAD(big.regs.MSW, 0x00010001u, sum); big.pair = *__SIMD64(pSrc)++; sum = __SMLAD(big.regs.LSW, 0x00010001u, sum); sum = __SMLAD(big.regs.MSW, 0x00010001u, sum); } } else { /* Initialize accumulator to 0 */ sum = 0; } if (pSize & 0x4) { /* Deal with remaining 64 bits (4 samples) */ big.pair = *__SIMD64(pSrc)++; sum = __SMLAD(big.regs.LSW, 0x00010001u, sum); sum = __SMLAD(big.regs.MSW, 0x00010001u, sum); } if (pSize & 0x2) { /* Deal with remaining 32 bits (2 samples) */ pair = *__SIMD32(pSrc)++; sum = __SMLAD(pair, 0x00010001u, sum); } if (pSize & 0x1) { /* Deal with potential last 16 bits (1 sample) */ sum+= *pSrc++; } return (int16_t)(sum / (int32_t)pSize); }
And corresponding compiled code …
Final assembler;Buffer size = 4 MOVS r2,#0x00 ; 2 1 Initialize accumulator to zero LDRD r1,r0,[r0,#0] ; 4 3 Load 64-bits and don't update MOV r3,#0x10001 ; 4 1 Initialize constant coefficients SMLAD r1,r1,r3,r2 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two first samples by 1 and accumulate SMLAD r0,r0,r3,r1 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate ; Following 3 instructions emulate division behaviour : div rounds towards 0 on positive and negative numbers ASRS r1,r0,#31 ; 2 1 Get result sign ADD r0,r0,r1,LSR #30 ; 4 1 Add 3 if result is negative (0.75 after following shift) ASRS r0,r0,#2 ; 2 1 Shift result by 2 ROM : 26 bytes Stack : 0 bytes Cycles : 10 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ;Buffer size = 8 ADD r3,r0,#0x08 ; 4 1 Initialize a second pointer to pSrc + 8 LDRD r1,r2,[r0,#0] ; 4 3 Load 64-bits from pSrc and don't update MOV r0,#0x10001 ; 4 1 Initialize constant coefficients SMUAD r1,r1,r0 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two first samples by 1 and init accumulator SMLAD r12,r2,r0,r1 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate LDRD r1,r2,[r3,#0] ; 4 3 Load 64-bits from pSrc+8 and don't update SMLAD r1,r1,r0,r12 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate SMLAD r0,r2,r0,r1 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate ASRS r1,r0,#31 ; 2 1 Get result sign ADD r0,r0,r1,LSR #29 ; 4 1 Add 7 if result is negative (0.875 after following shift) ASRS r0,r0,#3 ; 2 1 Shift result by 3 ROM : 40 bytes Stack : 0 bytes Cycles : 15 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ;Buffer size = 13 ADD r1,r0,#0x08 ; 4 1 Initialize a second pointer to pSrc + 8 LDRD r3,r2,[r0,#0] ; 4 3 Load 64-bits from pSrc and don't update MOV r0,#0x10001 ; 4 1 Initialize constant coefficients SMUAD r3,r3,r0 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two first samples by 1 and init accumulator SMLAD r12,r2,r0,r3 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate LDRD r2,r3,[r1,#0] ; 4 3 Load 64-bits from pSrc+8 and don't update SMLAD r2,r2,r0,r12 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate SMLAD r12,r3,r0,r2 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate LDRD r2,r3,[r1,#0x08] ; 4 3 Load 64-bits from pSrc+8+8 and don't update SMLAD r2,r2,r0,r12 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate SMLAD r0,r3,r0,r2 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate LDRSH r1,[r1,#0x10] ; 4 2 Load last sample @ pSrc + 8 + 16 ADD r0,r0,r1 ; 2 1 Accumulate it ; Following 4 instructions emulate division using multiplication with a constant LDR r1,[pc,#216] ; 2 2 Load division constant 0x4EC4EC4F (2^34 / 13) SMULL r1,r0,r1,r0 ; 4 1 Multiply result by the constant, result on 64 bits ASRS r1,r0,#2 ; 2 1 Divide Most significant word by 4 SUB r0,r1,r0,ASR #31 ; 4 1 Add 1 if result is negative ROM : 62 bytes Stack : 0 bytes Cycles : 25 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ;Buffer size = 16 ADD r2,r0,#0x08 ; 4 1 Initialize a second pointer to pSrc + 8 LDRD r3,r1,[r0,#0] ; 4 3 Load 64-bits from pSrc and don't update MOV r0,#0x10001 ; 4 1 Initialize constant coefficients SMUAD r3,r3,r0 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two first samples by 1 and init accumulator SMLAD r12,r1,r0,r3 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate LDRD r1,r3,[r2,#0] ; 4 3 Load 64-bits from pSrc+8 and don't update SMLAD r1,r1,r0,r12 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate SMLAD r12,r3,r0,r1 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate LDRD r1,r3,[r2,#0x08] ; 4 3 Load 64-bits from pSrc+8+8 and don't update SMLAD r1,r1,r0,r12 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate SMLAD r3,r3,r0,r1 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate LDRD r1,r2,[r2,#0x10] ; 4 3 Load 64-bits from pSrc+8+16 and don't update SMLAD r1,r1,r0,r3 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate SMLAD r0,r2,r0,r1 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate ; Following 3 instructions emulate division using shift operation ASRS r1,r0,#31 ; 2 1 Get result sign ADD r0,r0,r0,LSR #28 ; 4 1 Add 15 if result is negative (0.9375 after following shift) ASRS r0,r0,#4 ; 2 1 Shift result by 4 ROM : 64 bytes Stack : 0 bytes Cycles : 25 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ;Buffer size = 32 PUSH {r3-r4} ; 2 3 Backup LDRD r3,r2,[r0,#0] ; 4 3 Load 64-bits from pSrc and don't update ADD r1,r0,#0x08 ; 4 1 Initialize a second pointer to pSrc + 8 MOV r0,#0x10001 ; 4 1 Initialize constant coefficients SMUAD r3,r3,r0 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two first samples by 1 and init accumulator SMLAD r4,r2,r0,r3 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate LDRD r3,r12,[r1,#0] ; 4 3 Load 64-bits from pSrc+8 and post-increment by 8 ADD r2,r1,#0x08 ; 4 1 Initialize a second pointer to pSrc + 8 + 8 SMLAD r1,r3,r0,r4 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate SMLAD r1,r12,r0,r1 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate MOVS r3,#0x02 ; 4 1 Initialize loop counter to 2 loop_head: LDRD r4,r12,[r2],#0x08 ; 4 3 Load 64-bits and post-increment by 8 SMLAD r1,r4,r0,r1 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate SMLAD r4,r12,r0,r1 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate LDRD r1,r12,[r2],#0x08 ; 4 3 Load 64-bits and post-increment by 8 SMLAD r1,r1,r0,r4 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate SMLAD r1,r12,r0,r1 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate SUBS r3,r3,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter BCS loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) ASRS r0,r1,#31 ; 2 1 Get result sign ADD r0,r1,r0,LSR #27 ; 4 1 Add 31 if result is negative (0.96875 after following shift) ASRS r0,r0,#5 ; 2 1 Shift result by 5 POP {r3-r4} ; 2 3 Restore backed up registers ROM : 80 bytes Stack : 8 bytes Cycles : N=32 : 63 N power of 2 : 17 + (N/8 - 2) * 14 + 12 + 6 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ;Buffer size = 100 PUSH {r3-r4} ; 2 3 Backup LDRD r3,r2,[r0,#0] ; 4 3 Load 64-bits from pSrc and don't update ADD r1,r0,#0x08 ; 4 1 Initialize a second pointer to pSrc + 8 MOV r0,#0x10001 ; 4 1 Initialize constant coefficients SMUAD r3,r3,r0 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two first samples by 1 and init accumulator SMLAD r12,r2,r0,r3 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate LDRD r2,r3,[r1],#0x08 ; 4 3 Load 64-bits from pSrc+8 and post-increment by 8 SMLAD r2,r2,r0,r12 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate SMLAD r3,r3,r0,r2 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate MOVS r2,#0x0A ; 4 1 Initialize loop counter to 10 loop_head: LDRD r4,r12,[r1],#0x08 ; 4 3 Load 64-bits and post-increment by 8 SMLAD r3,r4,r0,r3 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate SMLAD r4,r12,r0,r3 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate LDRD r12,r3,[r1],#0x08 ; 4 3 Load 64-bits and post-increment by 8 SMLAD r12,r12,r0,r4 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate SMLAD r3,r3,r0,r12 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate SUBS r2,r2,#1 ; 2 1 Decrement loop counter BCS loop_head ; 2 3,1 Loop (3 cycles) or go through (1 cycle) LDRD r2,r1,[r1,#0] ; 4 3 Load final 64-bits and don't update SMLAD r2,r2,r0,r3 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate SMLAD r0,r1,r0,r2 ; 4 1 Parallel multiply two following samples by 1 and accumulate ; Following 4 instructions emulate division using multiplication with a constant LDR r1,[pc,#44] ; 2 2 Load division constant 0x51EB851F (2^37 / 100) SMULL r1,r0,r1,r0 ; 4 1 Multiply result by the constant, result on 64 bits ASRS r1,r0,#5 ; 2 1 Divide Most significant word by 32 SUB r0,r1,r0,ASR #31 ; 4 1 Add 1 if result is negative POP {r3-r4} ; 2 3 Restore backed up registers ROM : 92 bytes Stack : 8 bytes Cycles : 195
Summary (no division ¹) :
| Impl. | max ROM | max Stack | Cycle Formula (Power of 2) | 4 sps | 100 sps |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 40 bytes | 0 bytes | 3 + 10 * (N/2-1) + 11 | 14 cycles | 507 cycles |
| SMLAD3 | 48 bytes | 0 bytes | 3 + 10 * (N/4-1) + 11 | 11 cycles | 256 cycles |
| Final | 92 bytes | 8 bytes | 17 + 14 * (N/8-2) + 18 | 10 cycles | 195 cycles |
¹: When inlining, compiler optimizes division operation using fractional mutliplication.
Now, we reached what seems to be the optimal result in terms of cycles for all possible buffer sizes. Let’s compare all these results!
Overall comparison
For this overall comparison, I will not take all figures, only significant ones:
- Plain C optimized for time (-O3 -Otime): this is the original reference
- CMSIS implementation (arm_mean_q15), the intended one (see this paragraph if you don’t see what I’m talking about)
- SMLAD unroll by 4 implementation
- Same Plain C inlined with constant buffer size (-O3 -Otime)
- My final implementation
Following graph shows results in terms of total execution cycles per buffer size:
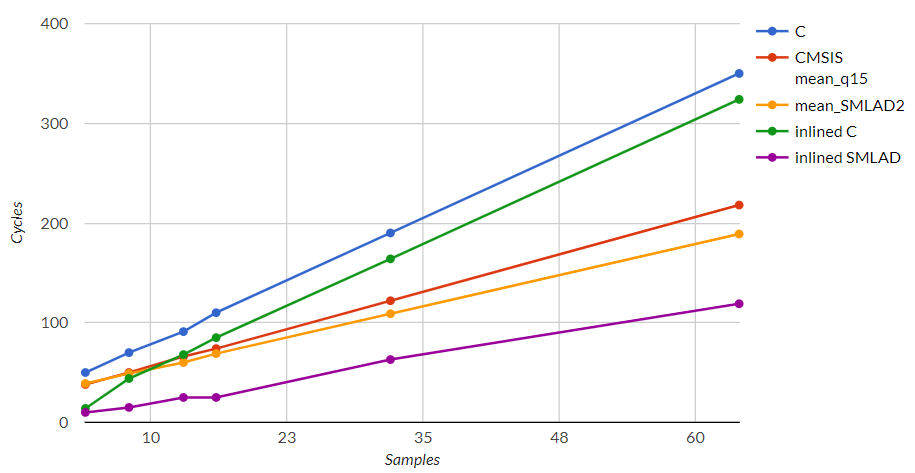
We can see that no matter buffer size, last implementation is the most effective by far.
Next graph shows results in terms of execution cycles per sample:
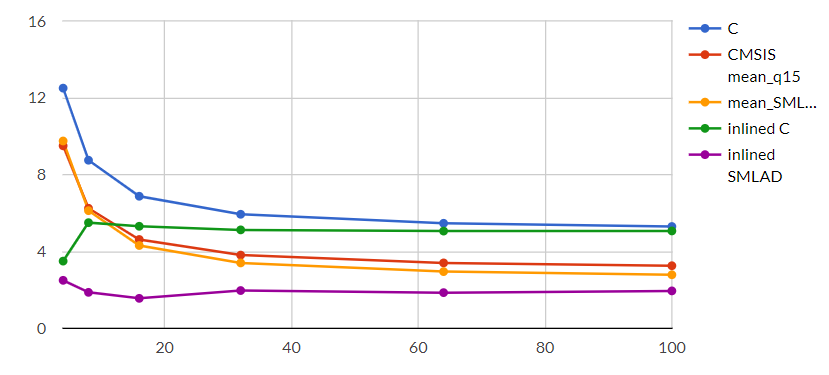
In-lining effect is very noticeable for small buffers (overhead cost is very comparable to effective computation cost), then all curves tend to a value which is only determined by loop content (=numberofcyclesperlooptreatedsamplesperloop). Using DSP extension « Dual signed multiply, add and accumulate (SMLAD) » and « Load Doubleword (LDRD) », most effective cycles per sample would be 3+1+14=1.25cycles/sample. It could be reachable if size was not important at all: you would just need 12 bytes per 4 samples packet!
Finally, following graph shows gain factors in terms of execution time compared to Plain C optimized for time (Bigger is better):
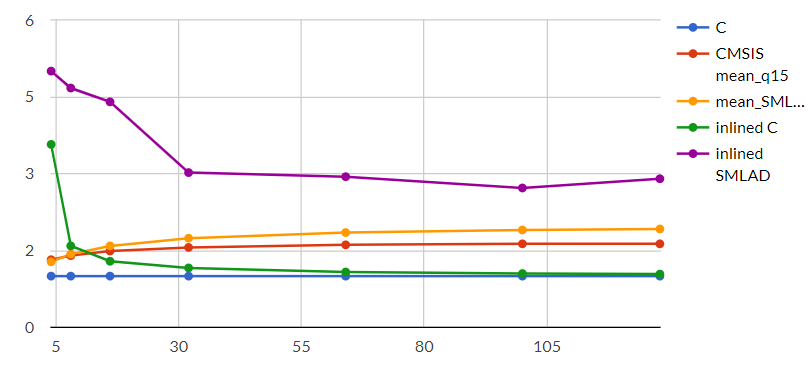
Looking at this, we can extract a very impressive figure: execution time has been divided by 2.7!
And we have just looked into a very simple algorithm: average !
I let you imagine what we can do using this awesome DSP extension on our Cortex M4 and Cortex M7!

nice article, looking forward for new ones.
J’aimeJ’aime
Thanks,
Next article is ongoing and it will deal with parallel comparison.
J’aimeJ’aime
Can you give me the reference where you got the ARM instruction set support with the KEIL unsupported instructions blacked out?
J’aimeJ’aime
Hi Richard.
There is no external reference to give, this blacklist comes from my observations of compiler outputs.
The list contains all Saturating instructions, bit/byte reversal, rotations as well as all parallel instructions.
No C compiler I crossed was able to take advantage of such instructions and Keil ARM compiler was the one I found better at reaching most instructions.
In fact, I believe the reason is that there is no way to describe these operations in C code.
J’aimeJ’aime
Good article!
Do you know some way to know the ROM, Stack and Cycles used by functions?
How did you do that in these cases?
J’aimeJ’aime
Short answer, manually …
For cycles, you can also execute your code on a simulator (IAR one is quite simple to use) and look at the core cycle counter.
ROM
I use assembly listing files to display both binary encoding instructions and their disassembled meaning. This gives me each instruction size and their sum the function size.
Stack
Regarding stack, you only need to look at PUSH/POP instructions, counting number of registers that are backup on stack (sometimes, compiler also directly manipulate stack with LDR/STR instructions, but it is easy to see since addressing is done using SP register).
Cycles
Finally, for cycles I initially looked into ARM® Cortex®‑M4 Processor Technical Reference Manual (3.3.1 Table of processor instructions) but these are really easy figures to remember since all data processing instructions take 1 cycle (except divisions) on a Cortex M4, then Load/Store/Push/Pop 1+n cycles. For Branches I chose to use a constant 3 cycles cost (average between minimal 2 and maximal 4 cycles).
J’aimeJ’aime